Office > Excel > Excel 2019 > Content
Office > Excel > Excel 2019 > ContentExcel VBA random number generator no duplicates(absolutely unique) in specified range(download xslm)
If you want to generate no duplicate random numbers in batches in Excel, it is not easy to do it with formulas, but it is easy to do it with VBA. VBA is very flexible in generating random numbers, which can meet the requirements of generating a variety of random numbers. For example, you can generate the decimal or integer random numbers in a batch, a specified range of decimal or integer random numbers(including negative numbers).
You generate random numbers with VBA is usually divided into two steps, one is to create a form and add controls, and the other is to write code. If you don't need to operate on the form, you can directly edit the code, but not so flexible. The following is the two examples of random numbers generated by VBA. One is simple in function, the other is multi-functional, and can generate random numbers that meet various requirements in batches. They both provide generated documents for download.
I, Excel VBA random number: Generate fixed decimal random numbers with the specified number of rows and columns in batches
(I) Create a form and add controls
1. Create a form. In the Excel window, press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editing window, click "Insert", select "UserForm" in the pop-up menu, and create a new UserForm; click the textbox on the right of the "(Name)" in the "Properties" small dialog box, select the text inside and copy or enter the "GenerateRandomForm" as the form name; then click the textbox on the right of the "Caption", select the text inside, and copy the "Generate Random Numbers" as the Caption of form. The operation steps are shown in Figure 1:
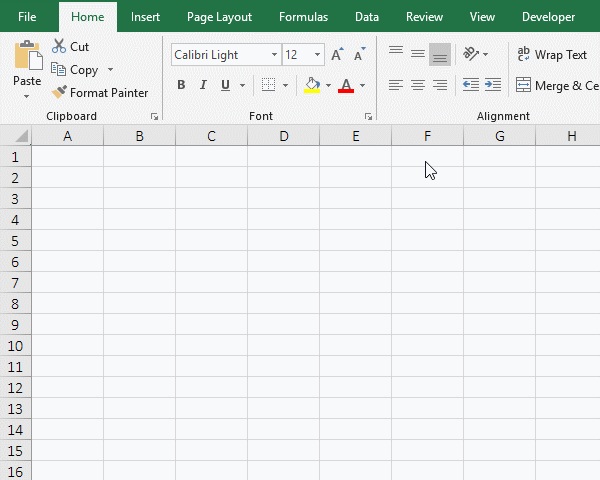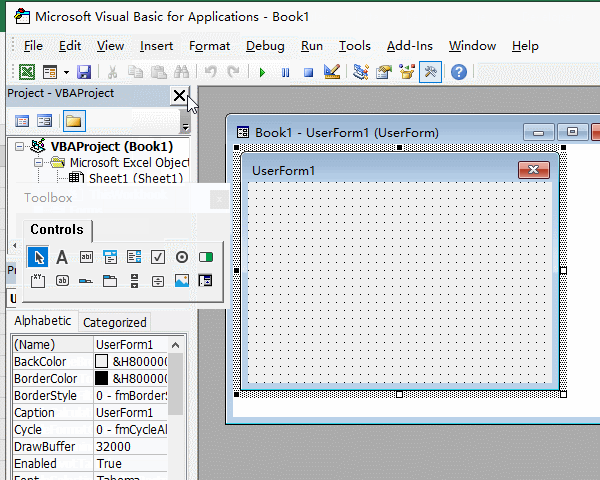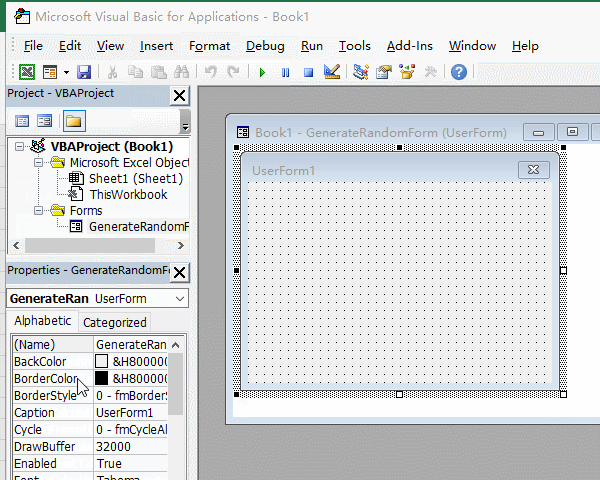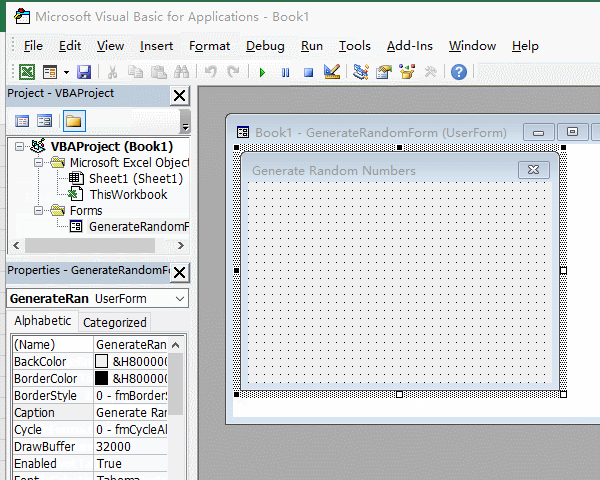
Figure 1
2. Add labels and textboxes controls.
A. Click the newly created form to display "Toolbox" on the left, move the mouse over the capital letter A, hold down the left button and drag to the form, then add a label control; change its "Name" to lblNumRows, and then change its "Caption" to "Rows:"; click the textbox to the right of the "Font", then click the "..." button on the right of the textbox to open the "Font" dialog box, and select 12 under the "Size", click "OK", set the font of the label to 12;
B. In the same way, drag a text box control(which has ab|) to the form, change its "Name" to "tbNumRows", and set its font to 12.
C. Hold Alt on the keyboard, click the label "Rows", select them, press Ctrl + C to copy, then press Ctrl + V to paste, and copy the "Label and TextBox"; click on the blank space of the form to release the selected state of the copies, select the copy "Rows", change its "Name" to lblNumCols, "Caption"to "Columns:"; then select the copied textbox, and change "Name" to "tbCols". Select the "Columns:", move the mouse to the right adjustment handle, after the mouse becomes a white double arrow, hold down the left button and drag to the right to make the text completely displayed. Select the two textboxes and drag to the right to increase their length in the same way. The operation steps are shown in Figure 2:
Figure 2:
3. Add button. Click the form of "Generate Random Numbers", drag a button control to the form, click the "Properties" small dialog box to hide the "ToolBox", change the button's "Name" to "cmdBtnSubmit", "Caption" to "Submit", and then set the font to 12; cick the blank space of the form, then select the button, press Ctrl + C to copy, then press Ctrl + V to paste the button, select the pasted button, change its "Name" to cmdBtnCancel, and then change its "Caption" to "Cancel". The operation steps are shown in Figure 3:
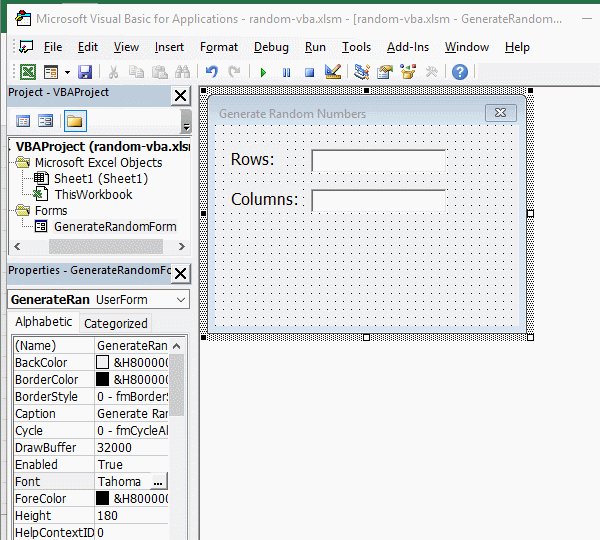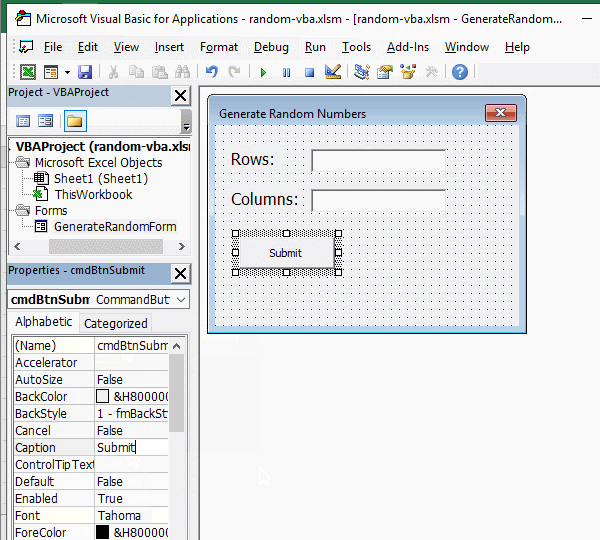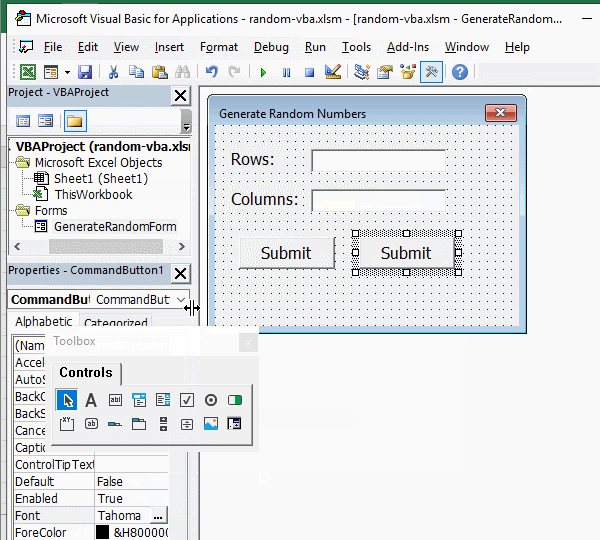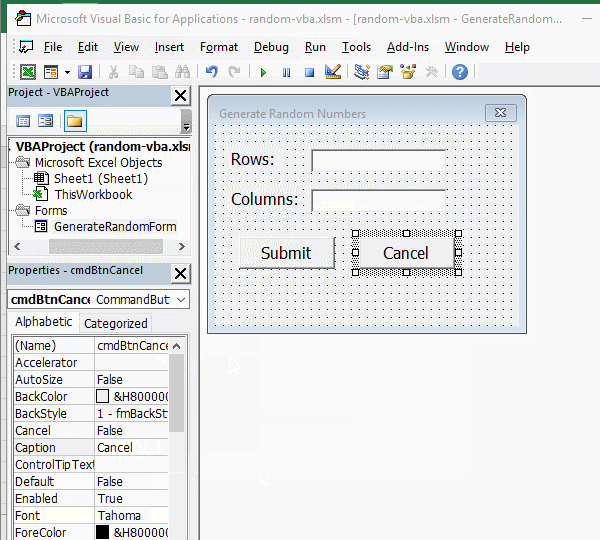
Figure 3
(II) Add code to the button and generate random numbers
1. Add code to the button. Double-click the "Submit" button to open the codes input window and copy the following code
Dim numRows As Integer
Dim numCols As Integer
'The number of rows and columns that have been inputted are converted to integers and assigned to numRows and numCols, respectively
numRows = Val(tbNumRows.Text)
numCols = Val(tbNumCols.Text)
For i = 1 To numRows
For c = 1 To numCols
'Assign the generated random number to the cell in row i and column c
Cells(i, c) = Rnd()
Next
Next
into
Private Sub cmdBtnSubmit_Click()
End Sub
Double-click the "GenerateRandomForm" to return to the "Generate Random Numbers" form. Double-click the "Cancel" button to copy the "Unload Me" into
Private Sub cmdBtnCancel_Click()
End Sub
2. Generate random numbers. Click "Run", select "Run Sub/UseForm", open the "Generate Random Numbers" dialog box, and switch to the Excel window. Enter "Number of Rows" 8 and "Number of Columns" 3, and click "Submit", Then generate 8 rows and 3 columns of random numbers; click "Cancel" to end the codes running; the operation process steps, as shown in Figure 4:
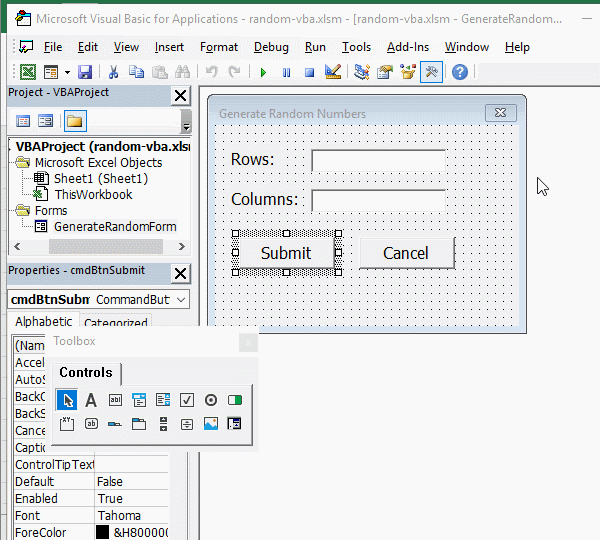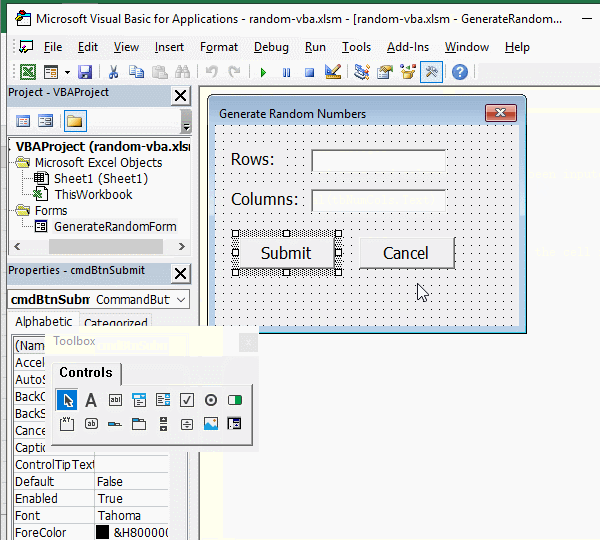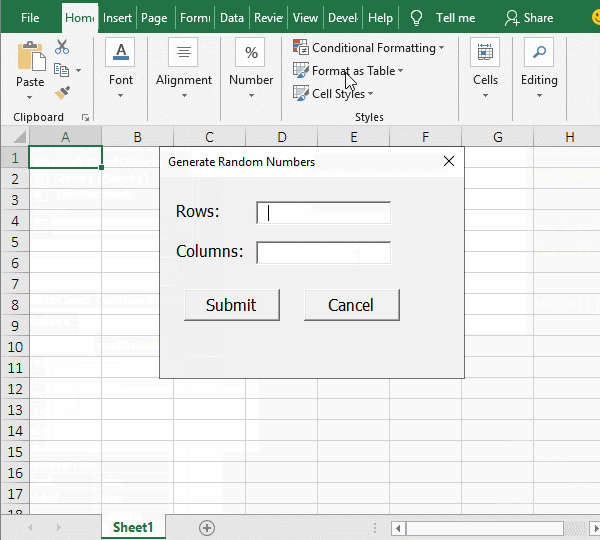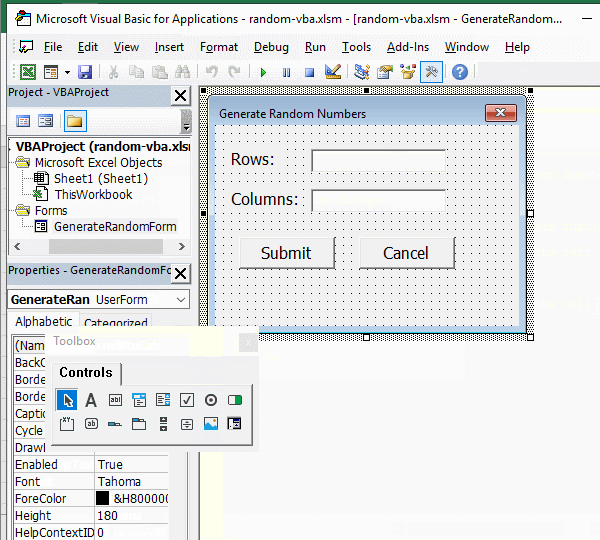
Figure 4
3. Code description:
A. The "Dim" are used to define variables. The "Dim numRows As Integer" defines "numRows" as an integer, and "numCols" is also defined as an integer.
B. The Val() function is used to convert the text to an integer, Val(tbNumRows.Text) converts the inputted "number of rows" to an integer.
C. The "For To Next" is loop statements. Two "For" loops are used in the code. The outer loop(For i = 1 To numRows) is used to control the number of rows to generate random numbers. The inner loop(For c = 1 To numCols) is used to control how many random numbers are generated in each row.
4. Download the Excel files that generate random numbers above: .xlsm version(Excel 2007 version), .xls version(Excel 2003 version). After downloading, open it with Excel, press Alt + F11 to switch to the VBA editing window, click "form" on the left side of the window to expand it, and then click the "GenerateRandomForm" to display the form, press F5 to run.
II, Excel VBA random number generator no duplicates(Generate customize absolutely unique random numbers in batches)
(I) Demo of generating random numbers
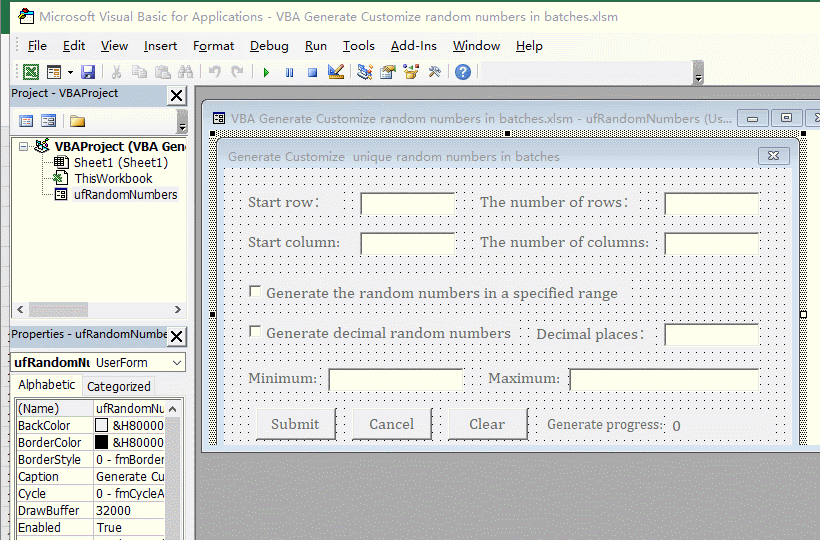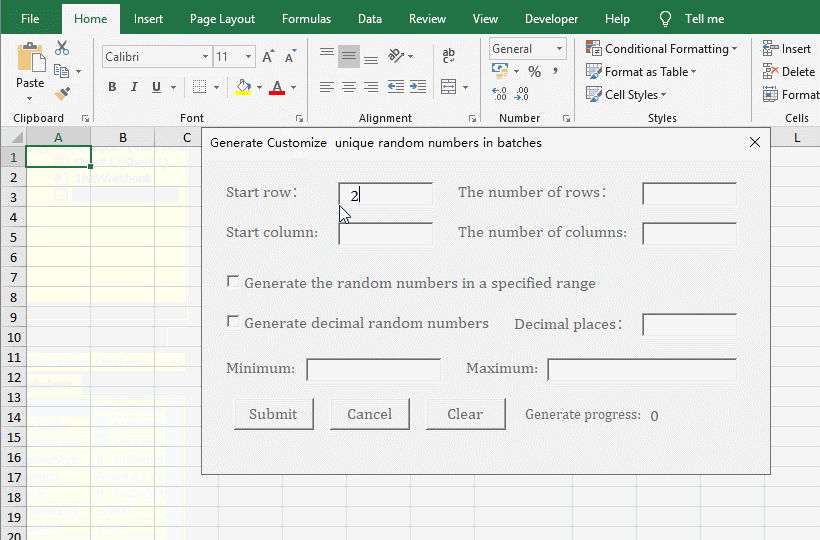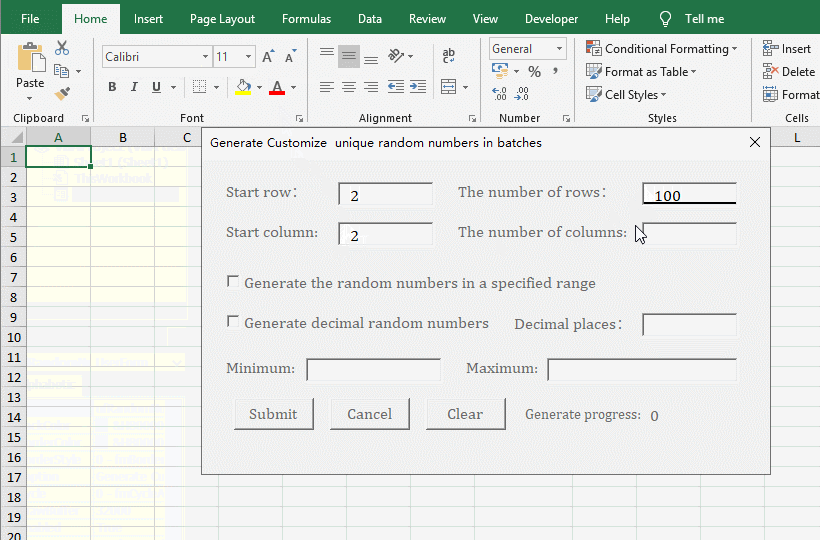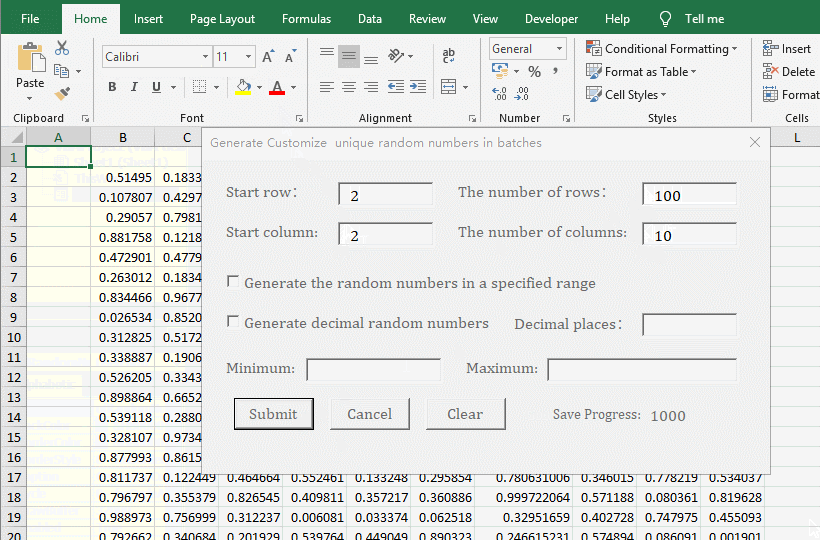
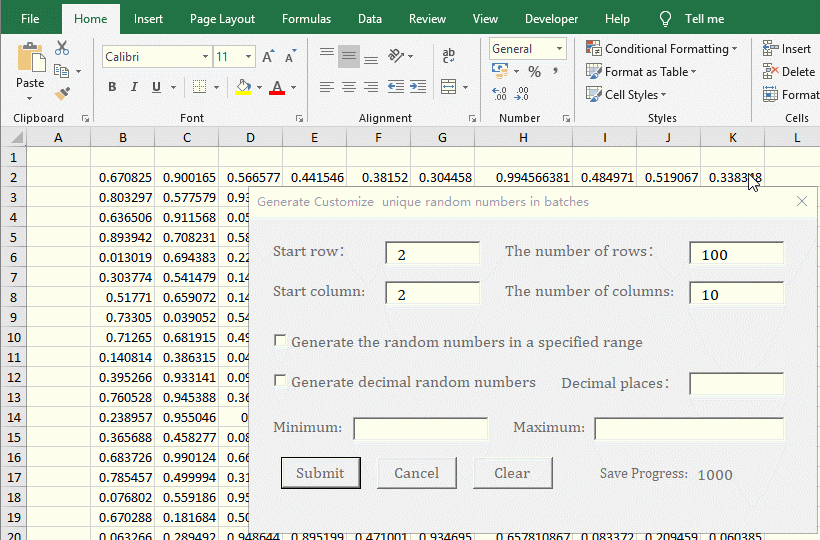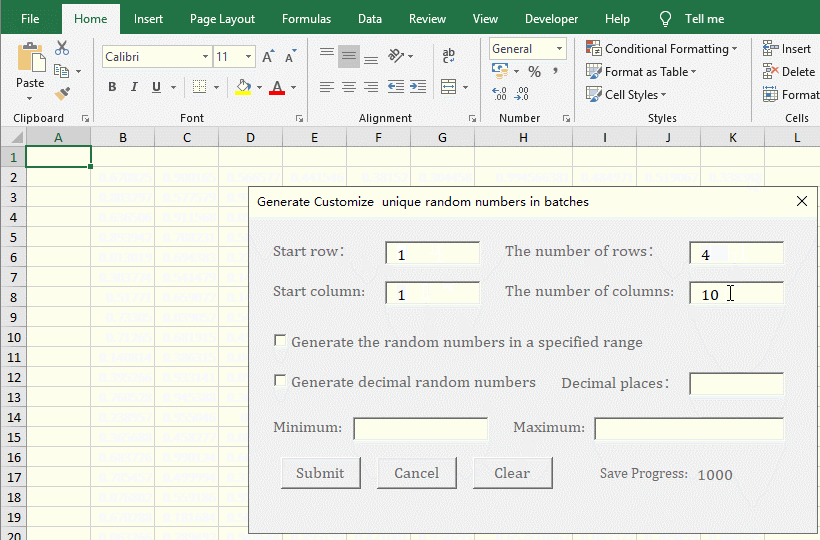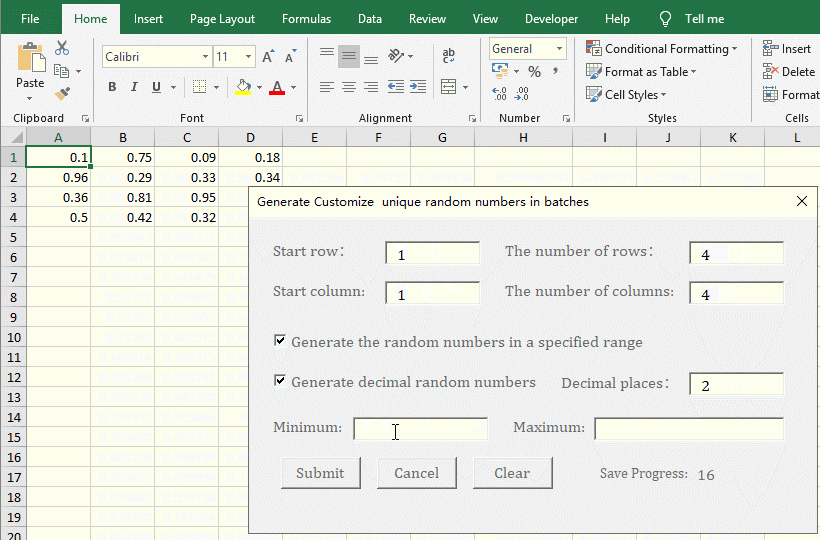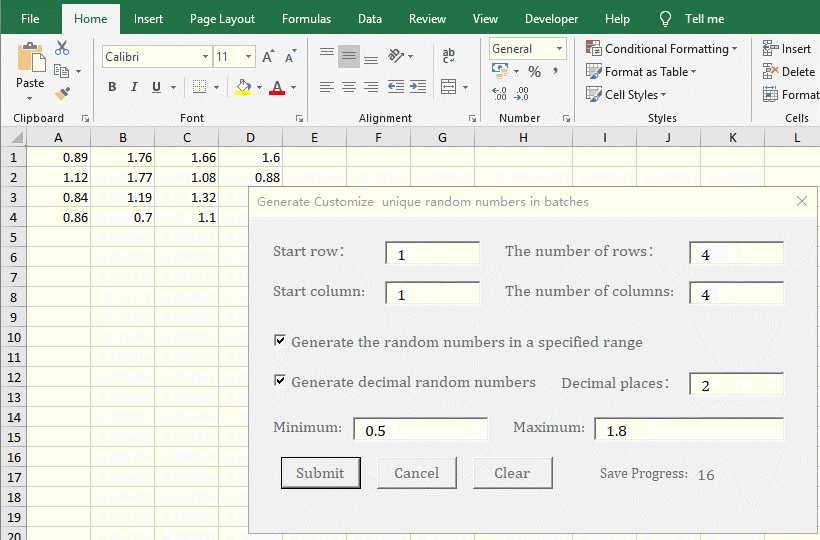
1. Generate the no duplicates decimal random numbers from 0 to 1 for the specified number of rows and columns. In the Excel window, press Alt + F11 to switch to the VBA editing window, click the "green right arrow" icon of "Run Sub/UserForm"(or press F5) to execute the code, open the "Generate customize unique random numbers in batches" dialog box and switch back to the Excel window. Enter 2 for the "Start Row and Start Column", enter 100 for "The number of Rows", enter 10 for "The number of Columns", and click "Submit" to generate 1000 decimal random numbers from 0 to 1. See screenshot in Figure 5:
Figure 5
2. Generate a unique random number with two decimal places. Click "Clear" to delete the random numbers last generated. The "Start row and Start column" are both changed to 1, and "The number of Rows and The number of Columns" are changed to 4, enter 2 for the "Decimal places", click the "Submit", 16 random numbers with two decimal places are generated. Check the "Generate the random numbers in a specified range", enter 0.5 for the "Minimum", 1.8 for the "Maximum", and click, "Submit" to generate 16 random numbers from 0.5 to 1.8 with two decimal places. The operation steps are shown in Figure 6:
Figure 6
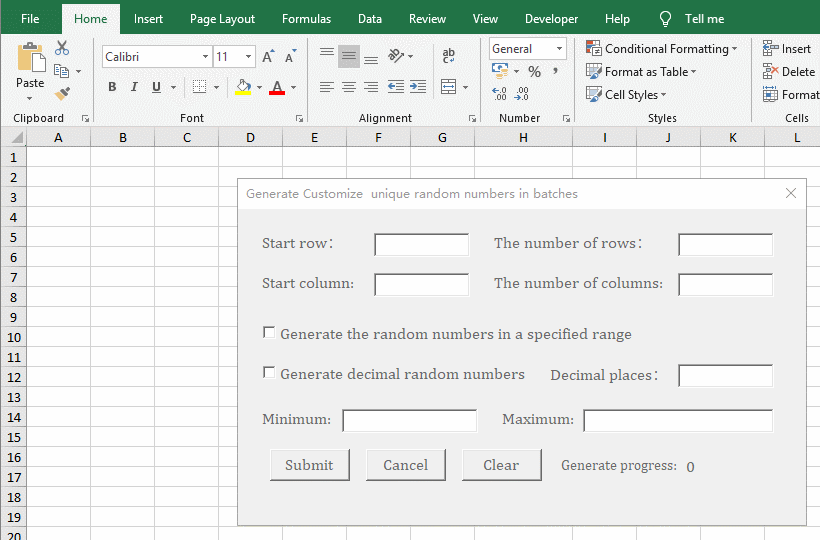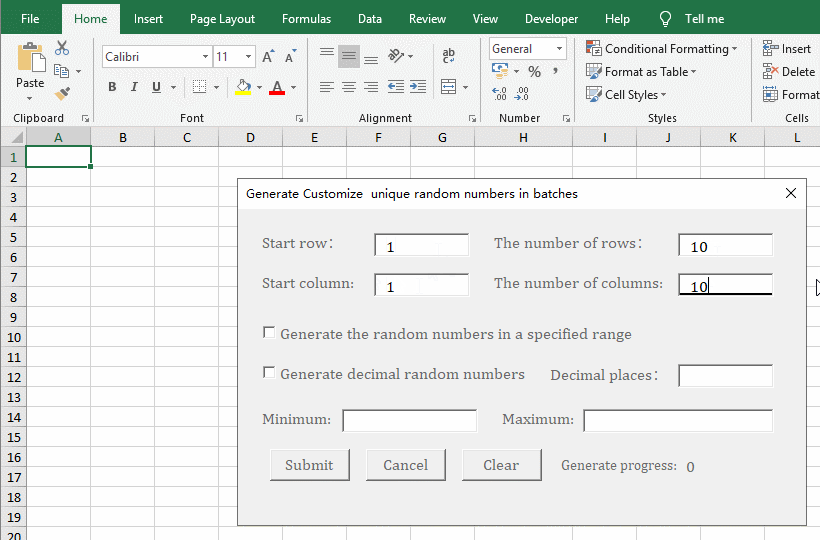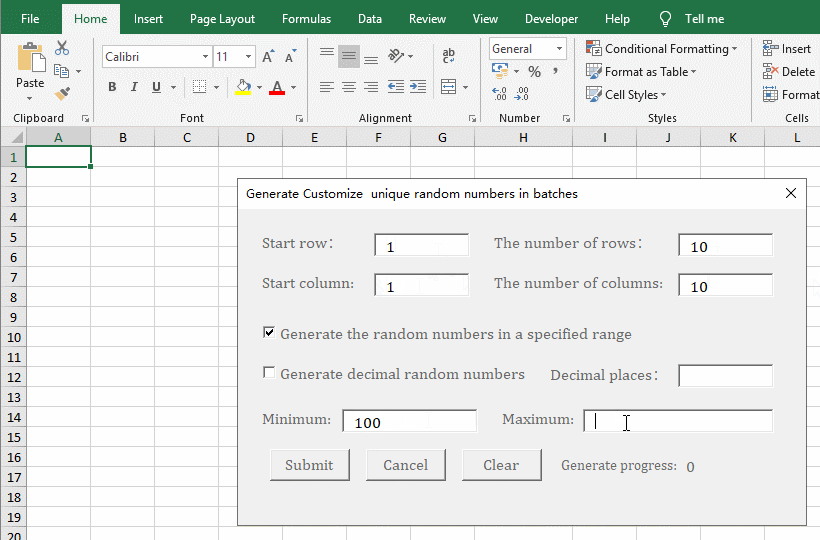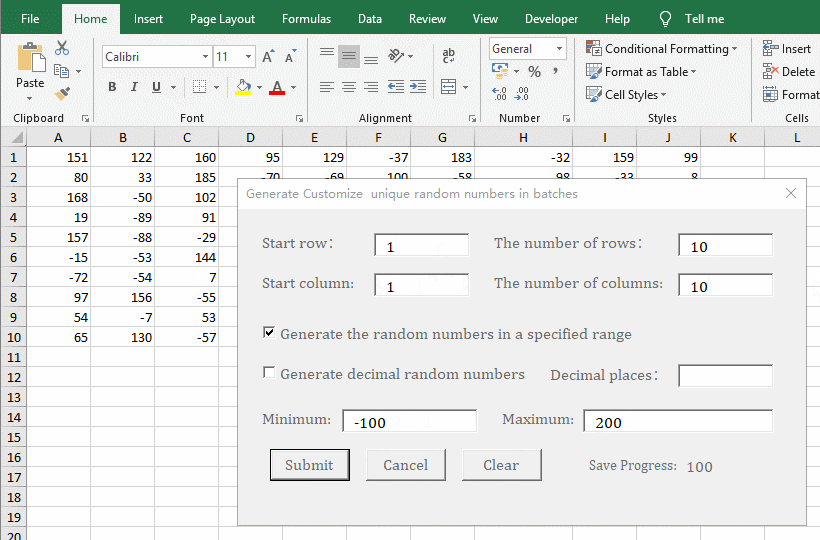
3. Generate unique integer random numbers in the specified range, number of rows, and number of columns. Enter 1 for the "Start Row and Start Column", enter 10 for "The number of Rows" and "The number of Columns", check "Generate the random numbers in a specified range", enter 100 for "Minimum", and enter 200 for "Maximum", click "Submit" to generate 100 integer random numbers from 100 to 200. Change the "Minimum" to -100 and leave the "Maximum" unchanged. "Click "Submit" to generate 100 integer random numbers from -100 to 200. The procedure is shown in Figure 7:
Figure 7
Tip: The number of random numbers that can be generated at one time is related to the computer memory. If the computer has more than 8 GB of memory, it can generate more than 1 million at a time. In addition, you must select the form or the code editing window before running the code. You cannot select a single control to run , This will cause an error.
(II) Create a form and add controls
Create a form and add controls as in the example above. Their "Name" and "Caption" are as follows:
"Start row" label: lblStartRow
"Start row" text box: tbStartRow
"Start column" label: lblStartColumn
"Start column" text box: tbStartColumn
"The number of rows" label: lblNumRow
"The number of rows" text box: tbRows
"The number of columns" label: lblColumns
"The number of columns" text box: tbColumns
"Generate the random numbers in a specified range" checkbox: cbRanBetween
"Generate decimal random numbers" checkbox: cbFloatRandom
"Decimal places" label: lblDecimalPlace
"Decimal places" text box: tbDecimalPlaces
"Minimum" label: lblMinimum
"Minimum" text box: tbMinimum
"Maximum" label: lblMaximum
"Maximum" text box: tbMaximum
Submit button: btnSubmit
"Cancel" button: btnCancel
"Clear" button: btnClear
"Generation progress" label: lblProgressText
"Number of current generations" label: lblProgressBar
"Error prompt" label: lblErrorr
(III) Add code to the button control
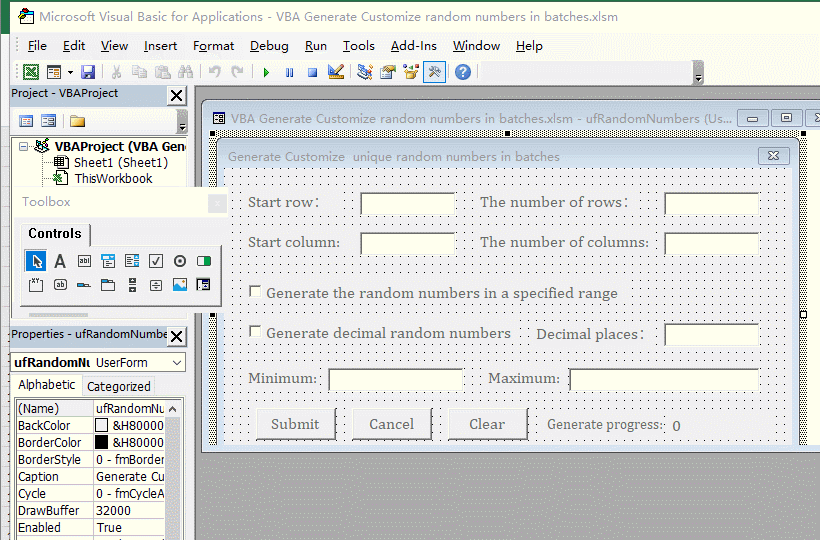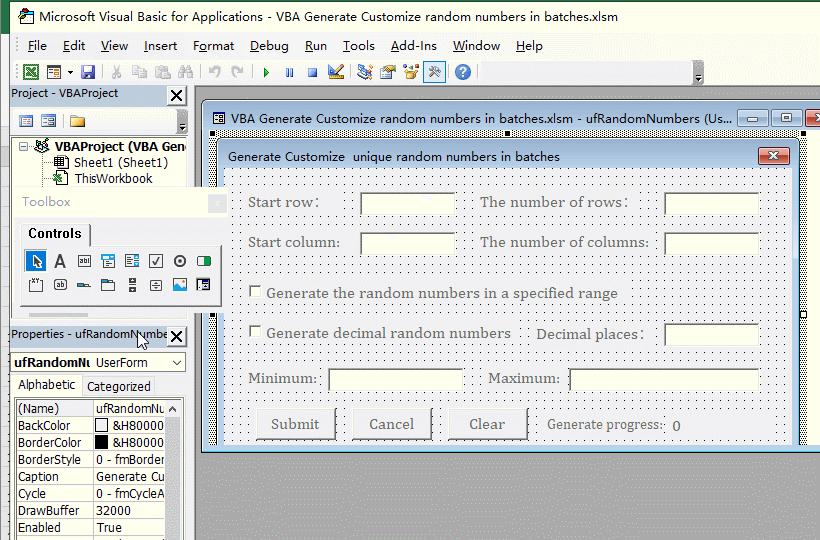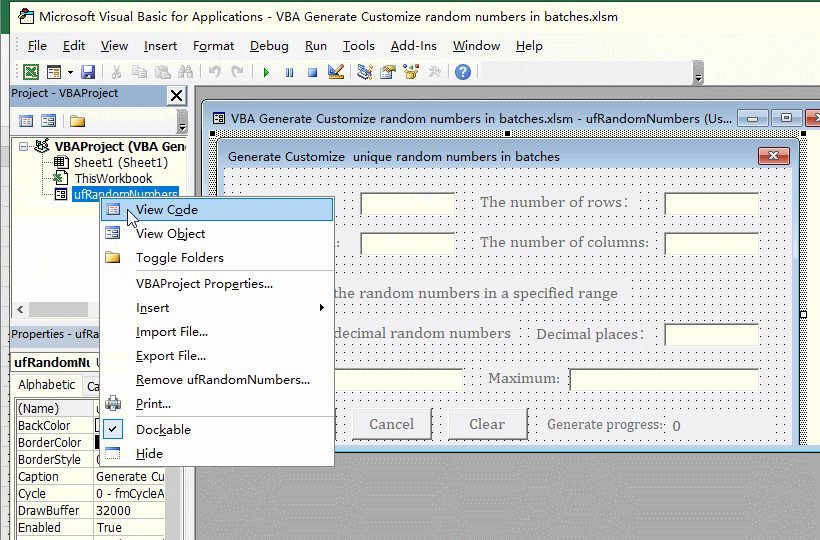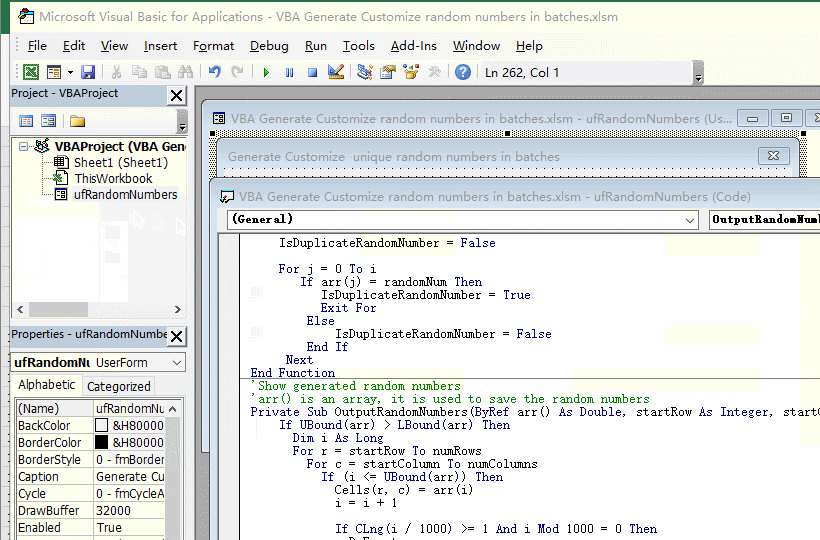
1. Click the "Form", then click "Properties" dialog to hide the "Toolbox", right-click the "ufRandomNumbers", select "View Code" from the pop-up menu, open the code editing window, and copy the following code:
Public flag As Boolean
Private Sub btnCancel_Click()
flag = True
Unload ufRandomNumbers
End Sub
Private Sub btnClear_Click()
Cells.Clear
End Sub
Private Sub btnSubmit_Click()
Dim startRow As Integer: startRow = 1
Dim numRows As Long 'The number of rows
Dim startColumn As Integer: startColumn = 1
Dim numColumns As Integer 'The number of columns
If tbStartRow.Text <> "" Then
If Not IsNumeric(tbStartRow.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The starting row must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
startRow = CInt(tbStartRow.Text)
End If
If tbRows.Text = "" Then
lblError.Caption = "The Number of rows cannot be empty!"
Exit Sub
End If
If Not IsNumeric(tbRows.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The number of rowss must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
numRows = CLng(tbRows.Text)
If tbStartColumn.Text <> "" Then
If Not IsNumeric(tbStartColumn.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The starting column must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
startColumn = CInt(tbStartColumn.Text)
End If
If tbColumns.Text = "" Then
lblError.Caption = "The number of columns cannot be empty!"
Exit Sub
End If
If Not IsNumeric(tbColumns.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The number of columns must be numeric!"
Exit Sub
End If
numColumns = CInt(tbColumns.Text)
If startRow <= 0 Then
startRow = 1
End If
If startColumn <= 0 Then
startColumn = 1
End If
Dim actNumRows As Long 'The actual number of rows
Dim actNumColumns As Integer 'The actual number of columns
actNumRows = numRows + startRow - 1 'Calculate the actual number of rows
actNumColumns = numColumns + startColumn - 1
Dim minimum As Double: minimum = 1 'The minimum of the specified range
Dim maximum As Double 'The maximum of the specified range
Dim strMsg As String: strMsg = " You can reduce the number of rows or columns, or increase the number of decimal places."
Dim decimalPlaces As Long: decimalPlaces = 0
Dim multiples As Long: multiples = 1
If (cbRanBetween.Value Or cbFloatRandom.Value) And tbDecimalPlaces.Text <> "" Then
If Not IsNumeric(tbDecimalPlaces.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The Decimal Places must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
decimalPlaces = CLng(tbDecimalPlaces.Text)
multiples = GetMultiples(decimalPlaces)
End If
If cbRanBetween.Value Then
If tbMinimum.Text <> "" Then
If Not IsNumeric(tbMinimum.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The minimum must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
minimum = CDbl(tbMinimum.Text)
End If
If Not IsNumeric(tbMaximum.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The maximum must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
maximum = CDbl(tbMaximum.Text)
If maximum < minimum Then
lblError.Caption = "The maximum must be greater than or equal to minimum!"
Exit Sub
End If
If cbFloatRandom.Value Then
If tbDecimalPlaces.Text = "" Then
decimalPlaces = 2
multiples = GetMultiples(decimalPlaces)
End If
If (maximum - minimum) * multiples + 1 < numRows * numColumns Then
lblError.Caption = "The numbers in specified range should be greater than or equal to " & numRows * numColumns & "." & strMsg
Exit Sub
End If
Else
If maximum - minimum + 1 < numRows * numColumns Then
lblError.Caption = "The numbers in specified range should be greater than or equal to " & numRows * numColumns & "." & strMsg
Exit Sub
End If
End If
Else
If decimalPlaces > 0 Then
If multiples < numRows * numColumns Then
lblError.Caption = "The numbers in decimal places range should be greater than or equal to " & numRows * numColumns & "." & strMsg
Exit Sub
End If
End If
End If
If lblError.Caption <> "" Then
lblError.Caption = ""
End If
flag = False
Dim arr() As Double
If lblProgressText.Caption = "Save Progress:" Then
lblProgressText.Caption = "Generate Progress:"
End If
Call CreateRandomNumbers(cbRanBetween.Value, cbFloatRandom.Value, decimalPlaces, numRows, numColumns, minimum, maximum, arr, lblProgressBar)
lblProgressText.Caption = "Save Progress:"
Call OutputRandomNumbers(arr, startRow, startColumn, actNumRows, actNumColumns, lblProgressBar)
End Sub
'Get multiples according to decimal places
Private Function GetMultiples(decimalPlaces As Long) As Long
If decimalPlaces <= 0 Then
GetMultiples = 0
Exit Function
End If
GetMultiples = 1
Dim i As Integer
For i = 0 To decimalPlaces - 1
GetMultiples = GetMultiples * 10
Next
End Function
'Generate the random numbers
'The "isBetweenRandom" means whether to generate a random number in the specified range, the "isFloatRandom" means to whether generate a decimal random number
Private Sub CreateRandomNumbers(isBetweenRandom As Boolean, isFloatRandom As Boolean, decimalPlaces As Long, numRows As Long, numColumns As Integer, minimum As Double, maximum As Double, ByRef arr() As Double, lblProgressBar As Object)
Randomize (Timer)
Dim endFlag As Boolean
endFlag = True
Dim totalCells As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim typeRandom As Integer
totalCells = numRows * numColumns
ReDim Preserve arr(0 To totalCells - 1)
If isBetweenRandom Then
If isFloatRandom Then
typeRandom = 1
Else
typeRandom = 2
End If
Else
If isFloatRandom And decimalPlaces > 0 Then
typeRandom = 3
Else
typeRandom = 4
End If
End If
For i = 0 To totalCells - 1
endFlag = GeneratorRandomNumberNoDuplicates(typeRandom, minimum, maximum, decimalPlaces, i, arr)
If flag Then Exit For
If CLng(i / 100) >= 1 And i Mod 100 = 0 Then
DoEvents
lblProgressBar.Caption = i
End If
If flag Then Exit For
Next
lblProgressBar.Caption = i
End Sub
'Generate unique random numbersCreateRandomNumbers
Private Function GeneratorRandomNumberNoDuplicates(n As Integer, minimum As Double, maximum As Double, decimalPlaces As Long, i As Long, ByRef arr() As Double) As Boolean
Dim temp As Variant
Dim endFlag As Boolean
endFlag = True
Dim baseNumber As Double: baseNumber = 10000000
Do While (endFlag)
If n = 1 Then 'Generate decimal random numbers in a specified range
temp = WorksheetFunction.Round(WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(minimum * baseNumber, maximum * baseNumber) / baseNumber, decimalPlaces)
ElseIf n = 2 Then 'Generate integer random numbers in a specified range
temp = Int(Rnd * (maximum - minimum + 1) + minimum)
ElseIf n = 3 Then 'Generate decimal random numbers that are round up to the specified decimal places
temp = WorksheetFunction.Round(Rnd, decimalPlaces)
Else 'Generate decimal random numbers
temp = Rnd
End If
endFlag = IsDuplicateRandomNumber(temp, arr)
If endFlag = False Then
arr(i) = temp
End If
Loop
End Function
'Check the currently generated random number is a duplicate
Private Function IsDuplicateRandomNumber(randomNum As Variant, ByRef arr() As Double) As Boolean
Dim i As Long
i = UBound(arr)
IsDuplicateRandomNumber = False
For j = 0 To i
If arr(j) = randomNum Then
IsDuplicateRandomNumber = True
Exit For
Else
IsDuplicateRandomNumber = False
End If
Next
End Function
'Show generated random numbers
'arr() is an array, it is used to save the random numbers
Private Sub OutputRandomNumbers(ByRef arr() As Double, startRow As Integer, startColumn As Integer, numRows As Long, numColumns As Integer, lblProgressBar As Object)
If UBound(arr) > LBound(arr) Then
Dim i As Long
For r = startRow To numRows
For c = startColumn To numColumns
If (i <= UBound(arr)) Then
Cells(r, c) = arr(i)
i = i + 1
If CLng(i / 1000) >= 1 And i Mod 1000 = 0 Then
DoEvents
lblProgressBar.Caption = i
End If
End If
lblProgressBar.Caption = i
If flag Then Exit For
Next
If flag Then Exit For
Next
Erase arr
End If
End Sub
Operation process steps, as shown in Figure 8:
Figure 8
(IV) Code analysis:
1. General description.
The "flag" defined at the beginning of the code is a global variable used to terminate the generation of random numbers; btnCancel_Click () is the execution event of the "Cancel" button; Sub btnClear_Click is the execution event of the "Clear" button; btnSubmit_Click () is the execution event of the "Submit" button .
2. Define variables and initialize them.
The code "Dim startRow As Integer: startRow = 1" defines startRow as an integer and initializes it to 1.
3. If statement.
The "If condition Then code End If" or "If condition Then code Else code End If" is a judgment statement. When the condition is true, the code after "Then" is executed, otherwise the code after "Else" is executed, and if there is no Else, it is not executed.
4. Input check.
To avoid code occurrent errors by the input content, we usually check whether the input content meets the code execution specifications. Here, you must enter the values, otherwise the code will occurrent an error, so you must check whether the contents of each textbox are numeric. The following is the code that checks whether the "Start row" is numeric:
If tbStartRow.Text <> "" Then
If Not IsNumeric(tbStartRow.Text) Then
lblError.Caption = "The Start row must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
Because the default value of the "Start row" is set to 1, it is not required to be entered, so only the text entered in the textbox of the "Start row" is used to determine whether the entered text is a numeric value. The code "If tbStartRow.Text <> "" Then" is used for checking whether the "Start row" has entered text, the code means: if the "Start row" textbox is not equal to empty.
IsNumeric() is used to check whether the text is a number, IsNumeric(tbStartRow.Text) is used to determine whether the text entered in the textbox of "Start Line" is a number. The "Not" is used to represent the "not" operation in VBA, The code "Not IsNumeric(tbStartRow.Text)" means: If the text in the textbox of "Start row" is not a number, then "the text in the textbox of Start row must be a number!" is returned to the user.
5.Type conversion
CInt() is used to convert string to integer, such as startRow = CInt(tbStartRow.Text) in the code, or Val(), such as startRow = Val(bStartRow.Text).
CLng() is used to convert string to long integer, such numRows = CLng(tbRows.Text) in the code.
6. Character or string concatenation
Connect characters, strings, or variables with the "&" symbol in VBA, such as "The numbers in specified range should be greater than or equal to " & numRows * numColumns & "." & strMsg.
7. Define a dynamic array or parameter
You need to define a common array before defining a dynamic array in VBA, and then redefine the common array to a dynamic array with the "ReDim Preserve", for example in the code:
Dim arr() As Double
TotalCells = numRows * numColumns
ReDim Preserve arr(0 To totalCells-1)
The "0 To totalCells-1" is the value range of elements of the dynamic array. If you use an array as a parameter, you need to the keywords "ByRef" that is used to pass address when you define it, such as "ByRef arr() As Double" in the code.
8. Determine whether the array is empty and take the length of the array
A. Compare the upper bound of the array with its lower bound to determine whether it is empty in VBA. If the upper bound is less than the lower bound, the array is empty, otherwise it is not empty; for example, the code "If UBound(arr)> LBound(arr) Then", the upper bound of the array "arr" is greater than its lower bound, so the "arr" is not empty. The "UBound()" function is used to get the upper bound of the array, and the "LBound()" is used to get the lower bound of the array.
B. Take the length of the array(that is, how many elements are in the array) with the "UBound (arr)", the "UBound(arr)" is the index of the last element of the array "arr". If you want to take the actual number of elements in the array, add 1, that is, UBound(arr) + 1.
9. Release the memory occupied by the array
After using the array, release the memory occupied by the array with the "Erase arr", especially when there are more elements or more content in the array, the "arr" is the name of the array.
10. Definition of controls as parameters
Control as a parameter needs to be defined as an object with the "Object". For example, the "Generation Progress" label control is defined as a parameter in the code as: lblProgress As Object.
11. Make the progress bar
A. You can use the label control(ie Label) to display the progress of the program. For example, the "lblProgressBar" is used to display the generated random numbers and save progress in real time. The code is as follows:
If CLng(i / 100)> = 1 And i Mod 100 = 0 Then
DoEvents
lblProgressBar.Caption = i
End If
B. the "CLng(i / 100)" is used to round with i and 100 in the code. When i is less than 100, the rounding result is 0. Only when i is greater than or equal to 100, the rounding result will be greater than or equal to 1. The fuction is to display the progress every 100 random numbers generated; the "i Mod 100" is used i and 100 to mod, that is, take the remainder. The fuction is to show the progress only if i is an integer such as 100 or 200.
C. There must be the "DoEvents" in the progress bar code, otherwise the progress will not change. In addition, you need to assign it again after the loop ends, such as in the code
Next
LblProgressBar.Caption = i
Otherwise, progress will not change.
12. End subprocess(function) and terminate program execution
A. End sub-process(function) execution. Take input checking as an example. When it is checked that the input content does not meet the specifications, end the execution of the current sub-process with the "Exit Sub", such as in the code:
If Not IsNumeric(tbStartColumn.Text) Then
LblError.Caption = "The starting column must be a number!"
Exit Sub
End If
B. Terminate program execution. When the form is closed with the "Unload Me" or Unload + "form name", if the program is not completed(such as the cycle is not completed), the program does not terminate execution, but continues to execute in the background and the foreground returns to ours is non-responsive. To terminate the execution of the program, we need to terminate the unfinished program. The variable "flag" is used as a flag to cancel the execution of the program in the example, if the user clicks the "Cancel" button, the "flag" is set to True immediately; If the "flag" is detected as True in the loop, the loop is ended immediately with the "Exit For"; the code is as follows:
Public flag As Boolean
Private Sub btnCancel_Click ()
Flag = True
Unload ufRandBetween
End Sub
If flag Then Exit For
13. Clear all cells
Clear all cells with VBA in Excel, you can use the "Cells.Clear", which will clear the contents and format of cells.
(V) Download Excel files: .xlsm version(Excel 2007 or later), .xls version (Excel 2003 version). After downloading, open it with Excel, press Alt + F11 to switch to the VBA editing window, click "form" on the left side of the window to expand it, and then click "ufRandomNumbers" to display the form, press F5 to run.
Hint: To execute VBA code, you need to check "Enable all macros", the method is: File → Options → Trust Center → Trust Center Settings → Macro Settings → Enable all macros → OK. In addition, when saving, select "Excel Macro-enabled Workbook" for "Save as type".
-
Related Reading
- How to move rows,columns,cells,table in excel(there
- Excel CountA and CountBlank function usage examples(
- How to freeze panes in excel and split window(15 exa
- How to use offset function in excel, include it and
- Excel pivot table percentage of grand total(parent r
- How to calculate average in excel, with quickly find
- Excel Countifs formula examples, include with And, O
- How to adjust row height and change width of column
- Excel If function examples, include if statement nes
- Excel SumIf function with ?/*, Average and array mul
- Excel substitute function usage(8 examples, with mul
- How to sort in excel(11 examples), include sort by c