Word temporary files location (Msocache folder takes up a lot of space)
Every software operation usually produces temporary files, and Word is no exception. Word generates temporary files, which are mainly used to recover documents when accidents occur. Of course, some of them may be temporary cache files. In addition, when installing Office, a lot of installation files will be cached in the Msocache folder, ranging from a few hundred megabytes to more than 1GB, which consumes hard disk space.
Where are the temporary saved Word files location? Different files and different Windows systems have different saving paths. In addition, not all temporary files can be deleted under any circumstances, so pay attention to the temporary files that can be deleted.
I. Word temporary files location
The location of the Word temporary file is different depending on the Windows version. Mainly the difference between XP and Win7 and above systems, which are introduced below.
1. Windows 7 and above system:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Word (login as an administrator, the login user name is generally Administrator). When you close Word without exception, you can delete it; if an accident occurs when you close Word, you'd better not delete it first, otherwise the unsaved document at the time of closing cannot be restored, as shown in Figure 1:
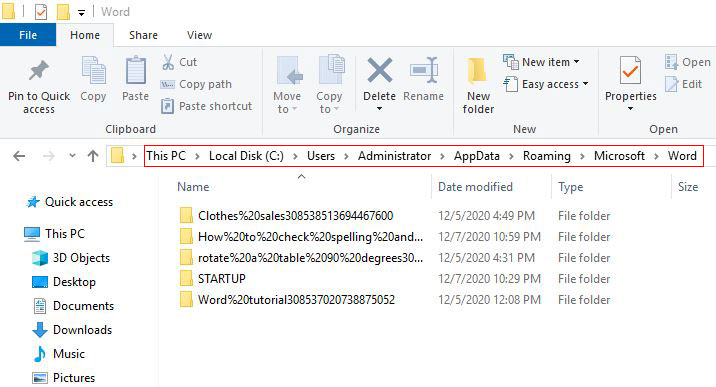
Figure 1
There is another location: C:\Users\login user name\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Office. Word temporary files are also stored. Delete them when the system disk is really out of space.
2. XP system:
C:\Documents and Settings\login user name\Application Data\Microsoft\Word (login as an administrator, the login user name is generally Administrator).
They can be deleted, please refer to Windows 7 and above system.
The temporary document files generated by Word will be deleted automatically when Word is closed normally, otherwise they will not be deleted automatically. You can delete them after restoring them.
II. Cached temporary files for installing Office (local installation source Msocache folder)
When installing Office, the local installation source first copies the installation files to the Msocache folder in the root directory of installation disk. If the installation file is one or two GB, it will take up so much hard disk space and will not be deleted automatically after the installation is complete. Once again, the Msocache folder is a system file (hidden), which is not easy to find. This causes the hard disk space to suddenly decrease a lot, but I don't know how small it is, and there is no way to release it.
If you install Office to the D drive, the local installation source will copy the installation files to the D:\Msocache folder, all files in it can be deleted.
How to display Msocache folder:
1. Windows 10 and 8: Open a File Explorer, select View tab in the ribbon → click Options icon → select View tab in the dialog box that has been opened → uncheck Hide protected operating system files → check Show hidden files, folders, and drives under Hidden files and folders → OK, as shown in Figure 2:
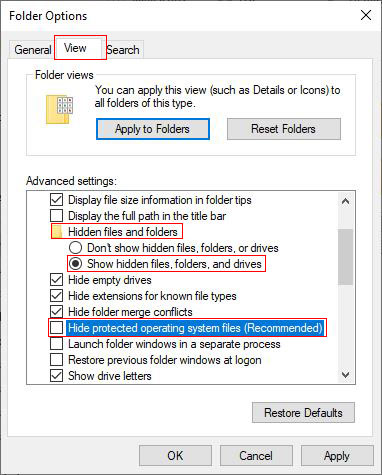
Figure 2
2. Windows 7: Open a File Explorer, select Organize → Folder and search options → View tab → uncheck Hide protected operating system files → check Show hidden files, folders, and drives under Hidden files and folders → OK, as shown in Figure 2:
3. XP system: Open a File Explorer, and select Tools menu → Folder option in turn. After setting method as with the Windows 7, just refer to Figure 2.
-
Related Reading
- How to delete table lines in Word (one line, remove
- How to add cross symbol and tick mark in Word, with
- Find ProPlusww.msi when opening Office(Word/Excel),
- How to set Header and footer in word(13 examples), i
- Word art transform text effect (Follow Path, Warp, A
- How to convert PowerPoint to word(4 examples), inclu
- How do I rotate a page 90 degrees in Word, with rota
- Can't print from microsoft Word (6 possible reasons)
- How to fix Microsoft Word has stopped working (sever
- How to make a table of contents in word and change,
- How to underline in word, with double, wave,long und
- How to delete a blank page in word(7 examples), incl
